Section 8.3 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
8.3: Precipitation Reactions
-
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 313274
A precipitation reaction is a reaction that yields an insoluble product—a precipitate—when two solutions are mixed. When a colorless solution of silver nitrate is mixed with a yellow-orange solution of potassium dichromate, a reddish precipitate of silver dichromate is produced.
\[ \ce{ AgNO_3(aq) + K_2Cr_2O_7(aq) \rightarrow Ag_2Cr_2O_7(s) + KNO_3(aq)} \label{4.2.1}\]
This unbalanced equation has the general form of an exchange reaction:
\[\ce{ AC + BD \rightarrow }\underset{insoluble}{\ce{AD}} + \ce{BC} \label{4.2.2}\]
Thus precipitation reactions are a subclass of exchange reactions that occur between ionic compounds when one of the products is insoluble. Because both components of each compound change partners, such reactions are sometimes called double-displacement reactions. Precipitation reactions are used to isolate metals that have been extracted from their ores, and to recover precious metals for recycling.
Video: Mixing potassium dichromate and silver nitrate together to initiate a precipitation reaction (Equation \(\ref{4.2.1}\)).
Just as important as predicting the product of a reaction is knowing when a chemical reaction will not occur. Simply mixing solutions of two different chemical substances does not guarantee that a reaction will take place. For example, if 500 mL of aqueous \(NaCl\) solution is mixed with 500 mL of aqueous \(KBr\) solution, the final solution has a volume of 1.00 L and contains \(\ce{Na^{+}(aq)}\)., \(\ce{Cl^{−}(aq)}\)., \(\ce{K^{+}(aq)}\)., and \(\ce{Br^{−}(aq)}\). As you will see in (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)), none of these species reacts with any of the others. When these solutions are mixed, the only effect is to dilute each solution with the other.
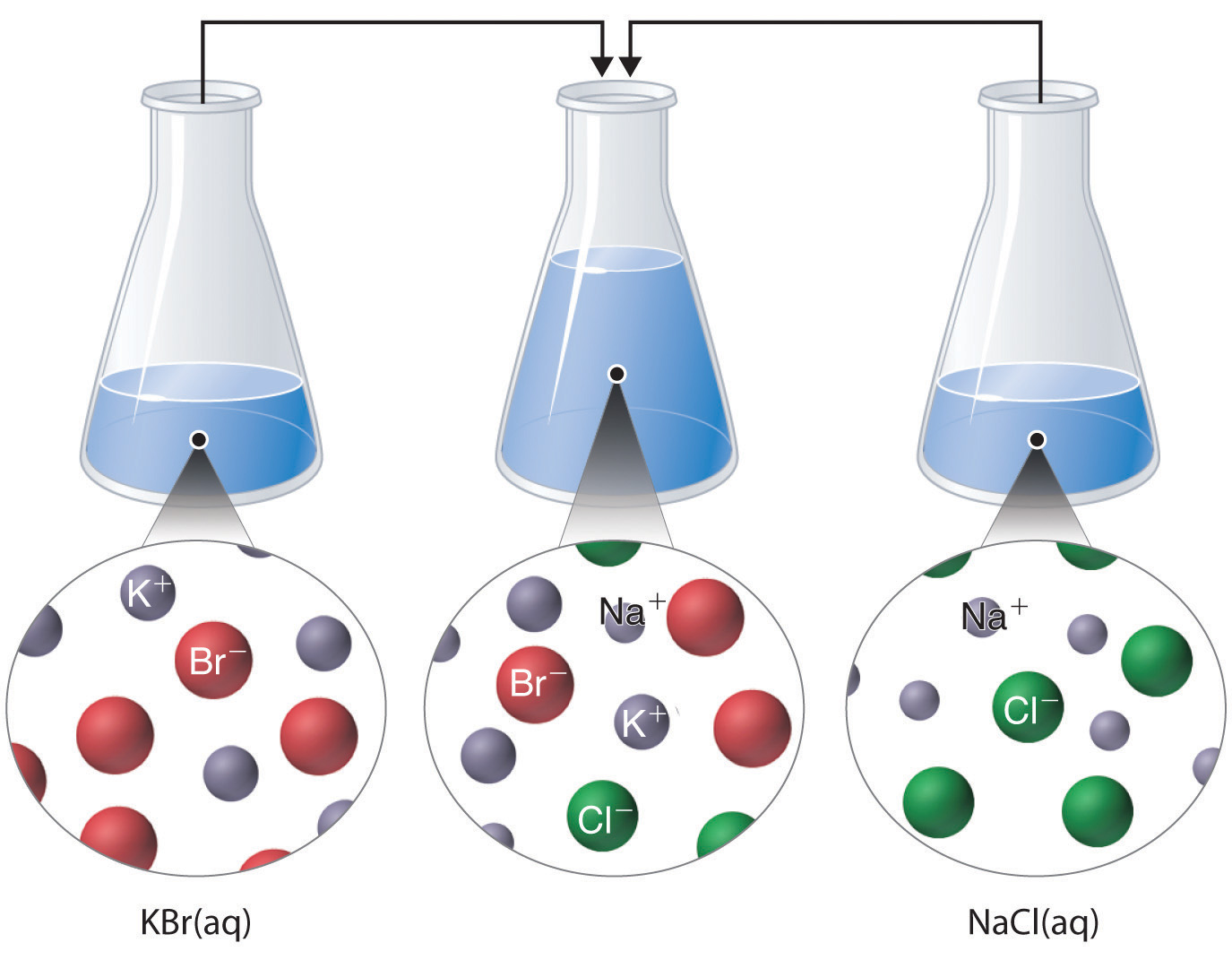
Predicting Precipitation Reactions
A precipitation reaction occurs when a solid precipitate forms after mixing two strong electrolyte solutions. As stated previously, if none of the species in the solution reacts then no net reaction occurred.
Predict what will happen when aqueous solutions of barium chloride and lithium sulfate are mixed.
Change the partners of the anions and cations on the reactant side to form new compounds (products):
Because barium chloride and lithium sulfate are strong electrolytes, each dissociates completely in water to give a solution that contains the constituent anions and cations. Mixing the two solutions initially gives an aqueous solution that contains Ba2 +, Cl−, Li+, and SO4 2− ions. The only possible exchange reaction is to form LiCl and BaSO4.
Correct the formulas of the products based on the charges of the ions.
No need to correct the formula as both compounds already have their charges balanced.
\[\ce{BaCl_2(aq) + Li_2SO_4(aq) \rightarrow BaSO_4 + LiCl} \nonumber \]
Refer to the solubility rules table to determine insoluble products which will therefore form a precipitate.
\[ \ce{BaCl_2(aq) + Li_2SO_4(aq) \rightarrow BaSO_4(s) + LiCl(aq)} \nonumber \]
Table 7.5.1 from the previous section shows that LiCl is soluble in water, but \(\ce{BaSO4}\) is not soluble in water.
Balance the equation:
\[\ce{BaCl_2(aq) + Li_2SO_4(aq) \rightarrow BaSO_4(s) + 2LiCl(aq)} \nonumber \]
Although soluble barium salts are toxic, \(\ce{BaSO4}\) is so insoluble that it can be used to diagnose stomach and intestinal problems without being absorbed into tissues. An outline of the digestive organs appears on x-rays of patients who have been given a "barium milkshake" or a "barium enema"—a suspension of very fine \(\ce{BaSO4}\) particles in water.
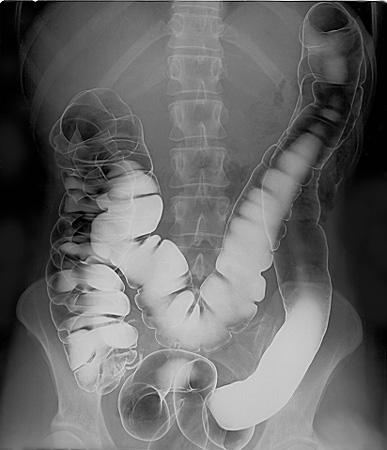
An x-ray of the digestive organs of a patient who has swallowed a "barium milkshake." A barium milkshake is a suspension of very fine BaSO4 particles in water; the high atomic mass of barium makes it opaque to x-rays. from Wikipedia.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Predict what will happen if aqueous solutions of rubidium hydroxide and cobalt(II) chloride are mixed.
Solution
| Steps | Example |
|---|---|
| Change the partners of the anions and cations on the reactant side to form new compounds (products). | 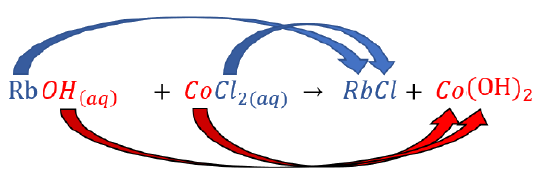 |
| Correct the formulas of the products based on the charges of the ions. | \(Rb(OH)_2(aq) + CoCl_2(aq) \rightarrow RbCl_2 + Co(OH)_2\) |
| Refer to the solubility rules table to determine insoluble products which will therefore form a precipitate. | \(Rb(OH)_2(aq) + CoCl_2(aq) \rightarrow RbCl_2(aq) + Co(OH)_2(s)\) |
| Balance the equation. | Coefficients already balanced. \(Rb(OH)_2(aq) + CoCl_2(aq) \rightarrow RbCl_2 + Co(OH)_2\) |
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Predict what will happen if aqueous solutions of strontium bromide and aluminum nitrate are mixed.
Solution
| Steps | Example |
|---|---|
| Change the partners of the anions and cations on the reactant side to form new compounds (products). | |
| Correct the formulas of the products based on the charges of the ions. | \(SrBr_2(aq) + Al(NO_3)_3(aq) \rightarrow Sr(NO_3)_2 + AlBr_3\) |
| Refer to the solubility rules table to determine insoluble products which will therefore form a precipitate. | \(SrBr_2(aq) + Al(NO_3)_3(aq) \rightarrow Sr(NO_3)_2(aq) + AlBr_3(aq)\) According to Table 7.5.1 from the previous section, both AlBr3 (rule 4) and Sr(NO3)2 (rule 2) are soluble. |
| If all possible products are soluble, then no net reaction will occur. | \(SrBr_2(aq) + Al(NO_3)_3(aq) \rightarrow\) NO REACTION |
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Using the information in Table 7.5.1 from the previous section, predict what will happen in each case involving strong electrolytes.
- An aqueous solution of strontium hydroxide is added to an aqueous solution of iron(II) chloride.
- Solid potassium phosphate is added to an aqueous solution of mercury(II) perchlorate.
- Solid sodium fluoride is added to an aqueous solution of ammonium formate.
- Aqueous solutions of calcium bromide and cesium carbonate are mixed.
- Answer a
- Fe(OH)2 precipitate is formed.
- Answer b
- Hg3(PO4)2 precipitate is formed.
- Answer c
- No Reaction.
- Answer d
- CaCO3 is precipitate formed.
-
Summary
In a precipitation reaction, a subclass of exchange reactions, an insoluble material (a precipitate) forms when two electrolyte solutions are mixed. To predict the product of a precipitation reaction, all species initially present in the solutions are identified, as are any combinations likely to produce an insoluble salt.
Section 8.3 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Portland_Community_College/CH104%3A_Allied_Health_Chemistry_I/08%3A_Types_of_Chemical_Reactions/8.03%3A_Precipitation_Reactions